In any market transaction between a seller and a buyer. The price of the product depends on the relationship between supply and demand. Understanding the law of supply and demand helps businesses make informed decisions to increase their profitability over a given period.
In this blog, we will understand how the law of supply and demand works and how businesses can generate consistent revenue without drying out their profit margins.
What is the law of supply and demand?
The law of supply and demand is a theory that explains the interaction between the seller of a resource (such as a product) and the buyer of that resource. This interaction determines the actual market price and market value of the goods.
Suppose you sell perfumes.
If demand for your perfumes goes up, maybe because of a new trend or a viral video, more people will want to buy from you. But since the supply is still the same, the price goes up because there are more buyers than bottles.
Now, once you see sales going crazy, you’ll probably order more perfumes from the manufacturer to meet that demand. So over time, the supply increases, but it’s the price that moved first because of the demand spike.
On the flip side, if people stop buying perfumes, demand drops. You’re left with unsold stock, so you start lowering prices to sell it off. And eventually, you’ll stop ordering more, which means supply goes down too, but again, after the price falls.
So yeah, price moves first, and supply usually reacts to it. That’s the real play between supply, demand, and price.
This theory is based on two different laws;
1- The law of supply
2- The law of demand
The law of demand
According to the law of demand, if all other factors remain constant, then the higher the price of the good, the fewer people will demand that good.
The demand is seen from the consumer perspective.
Higher the price of the product = Lower the quantity demanded
Customers want to get the most value for their money. That’s why when the prices increase, the demand drops. On the other hand, if prices drop, customers will be more willing to buy the product at the sale price, and demand will increase.
Also read about retail customers.
Factors affecting demand
1- Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences regarding your product depend on your product price. If the price increases, the demand will drop and vice versa. Therefore, there is a converse relationship between the demand for goods and their prices.
2- The existence and pricing of other substitutes and complementary goods
The price of a specific good depends on the price of other products as well. There are two types of products.
One is substitute product, when the price of the substitute product increases, the demand for the specific product also increase and vice versa.
The other products are complementary. When the price of a complementary product increases, the demand for the specific product decreases. If the price of electricity increases, the demand for electronic products like refrigerators and AC decreases.
3- Changes in condition that change consumer choices
Seasonal shifts and marketing also impact the demand for the product. If you sell products that are specifically for the winter season, the demand will increase as the season approaches.
Similarly, if you put a lot into marketing and advertising the product, it will create a perception of FOMO, and the demand for that product will increase over time.
4- Changes in the income of consumers
The demand for the product is directly proportional to the income of consumers. If, due to certain conditions, the income of consumers drops, the demand for the product will also drop.
The law of supply
In the law of supply, if all other factors remain constant, as the price of the goods increases, the supply of those goods will also increase. There is a linear relationship between the price of the goods and the supply needed.
The supply of goods ∝ The price of the goods
The supply line is seen from the seller’s perspective. When the price increases, the manufacturers will produce more goods to earn more profits and maintain equilibrium.
On the other hand, when prices drop, the manufacturer drops the production of the goods as they won’t be able to cover the cost of production

Factors that affect supply
1- Production cost
The supply of the good largely depends on its production costs, including labor costs, material costs, taxes, regulations, and other institutional costs. Therefore, any rise in these costs can impact the supply of goods. Alternatively, it can lead to an increase in the cost of goods being supplied, which ultimately affects the demand and price of those goods.
2- Impact of physical technology
The supply of goods is also impacted by the technology used in production or for other purposes. If you are using the latest technology that speeds up the production process and cuts lead times by up to 50%, then it makes the supply process much faster, impacting the demand for goods as well.
3- Number of sellers vs production capacity
If the producer of the goods supplies to multiple sellers but they don’t have the production capacity to meet all the demand in time, it means what they can produce in 3 days, due to higher demand, it will take them 5 days to deliver. Or they can limit the supply of goods to each seller, like instead of delivering 50 pieces of goods, they are only delivering 30 pieces. It impacts both the pricing of the product due to higher demand or limited supply of the goods.
The point of equilibrium
It’s the point where the supply and demand of the good meet. Here, the price is according to the market value of the good, not based on the difference in supply and demand.

Equilibrium price
Price is where the cost of producing goods (supply) meets the revenue generated by selling those goods (demand); that price is known as equilibrium price.
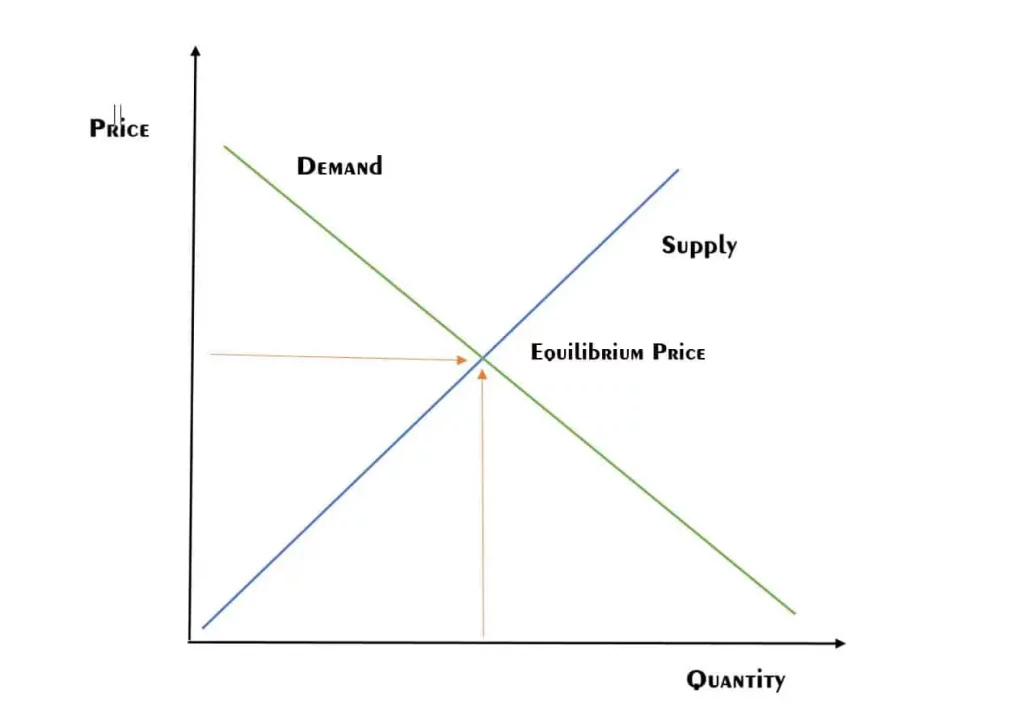
However, in real life, it’s not easy to achieve equilibrium prices due to multiple factors that have been discussed. Because both parties think about how they can get more benefits. Manufacturers want higher profits by selling goods at increased prices, while consumers look for lower prices and sales. Therefore, it is important to reach a balance where both parties, consumers and producers, benefit equally.
Other factors affecting supply and demand
1- Monopolies
Monopolies also affect the supply and demand of goods. When a single entity controls most of the supply, it has the power to influence both supply and demand. For example, during the launch of iPhones, increased demand and limited supply caused prices to be set very high to maximize profits. While this is seen as most beneficial for sellers, it is also considered an illegal practice.
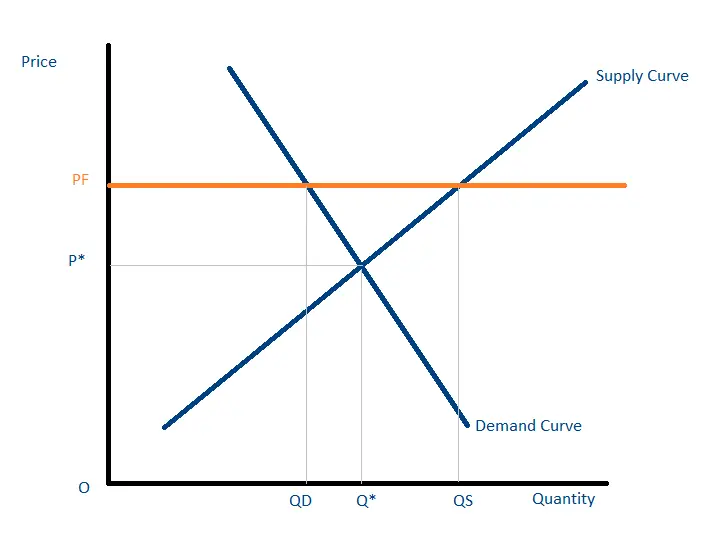
2- Price floors
Price floors are the minimum prices set by the government to protect vulnerable sellers. For example, on necessities like vegetables and fruits, government often applies price floors to help small sellers generate sales revenue regardless of larger competitors. When a price floor is set, no seller can sell that good for less than the specified threshold.
For instance, if the price floor on wheat is $18, no seller can sell it for less than that.
The absence of a price floor can create a significant imbalance between supply and demand. Without a price floor for wheat, the equilibrium price could drop far below $18, which could be harmful for small sellers as it sharply cuts their profit margins.
3- Subsidies
As an alternative to the price floor, subsidies cover the portion of production costs. This also helps create a balance between supply and demand.
In this way, the producer will have fewer costs to cover, earn a good sales revenue. And if we take above wheat example with subsidies, the small sellers will be able to manage a respectable living even if the pricing falls to the very low equilibrium prices.
3- Taxes
Taxes are the government-imposed price on goods to raise revenue. A tax on buyers means that the buyer has to buy goods at a price above the equilibrium price. In this way, the additional profits generated will go straight into government banks and be used to fund public infrastructure projects. Based on the tax imposed on the producer, the prices fluctuate, and so does the supply and demand of the goods.
Different scenarios that could happen to supply and demand
If you are still confused about how the relationship between supply and demand works, here’s a simple table.
| Demand | Supply | Price | Why It Happens (Scenario) |
| Increases | Stays the same | Increases | Product shortage leads to higher value |
| Decreases | Stays the same | Decreases | Too much product left causes value to drop |
| Stays the same | Increases | Decreases | Easy availability creates surplus, lowering the price |
| Stays the same | Decreases | Increases | Limited availability creates scarcity, raising the price |
Benefits of supply and demand
Apart from the impacts that an imbalance between supply and demand can cause, now it’s time to look at all the benefits producers, sellers, and consumers have due to this law and why it is considered important for any business to understand it.
1- It helps set the right product price
Understanding how supply and demand work helps both producers and sellers set the right price for their products, not too low to cut profit margins or too high to scare away consumers. In this way you set a right price that your market is willing to pay.
2- It helps in production decisions
Based on demand, producers can make supply decisions about how much product should be produced to meet that demand. Not too much overproduction or too little to create shortages, but the right amount to prevent costs and reduce waste.
3- It helps with market forecasting
Based on the demand for the product, producers can predict how much supply will be needed. This helps them forecast future market shifts. Therefore, by predicting the shifts, businesses can make informed decisions regarding where to invest, which products to scale, and which new markets to enter.
End note
If you are a manufacturer or a seller, understanding what the law of supply and demand is more than important to scale your business and generate healthy profit margins. To prevent overproduction or understocking, you can always use inventory management software that helps in forecasting and makes it easier for the business to meet the supply and demand on time and make the supply chain go smoothly.



